If you’re here, you’re probably trying to make sense of what offshoring really means and why so many businesses are doing it. At iScale Solutions, we get this question a lot. The answer? It’s not just a trend. Offshoring is a business practice that continues to gain momentum for companies that want to grow smarter, not just bigger.
As global competition heats up, offshoring allows companies to stay lean, cost-effective, and operationally agile by relocating business operations to strategic locations around the world.
So, What Is Offshoring?
Simply put, offshoring involves moving certain business functions like technical support, software development, or even manufacturing jobs to another country. This shift helps companies tap into skilled talent, reduce labor costs, and boost efficiency.
Unlike domestic cost-cutting, offshoring work opens the door to a global workforce while maintaining or even improving performance. Whether you’re handling services offshoring like customer service or production offshoring for physical goods, the goal is the same: do more with less.
Let’s put this into perspective:
Suppose your business is U.S.-based and you set up a customer support center in the Philippines. That’s a classic example of offshoring. You’re not just saving money—you’re improving service quality, thanks to a highly skilled and English-proficient workforce.
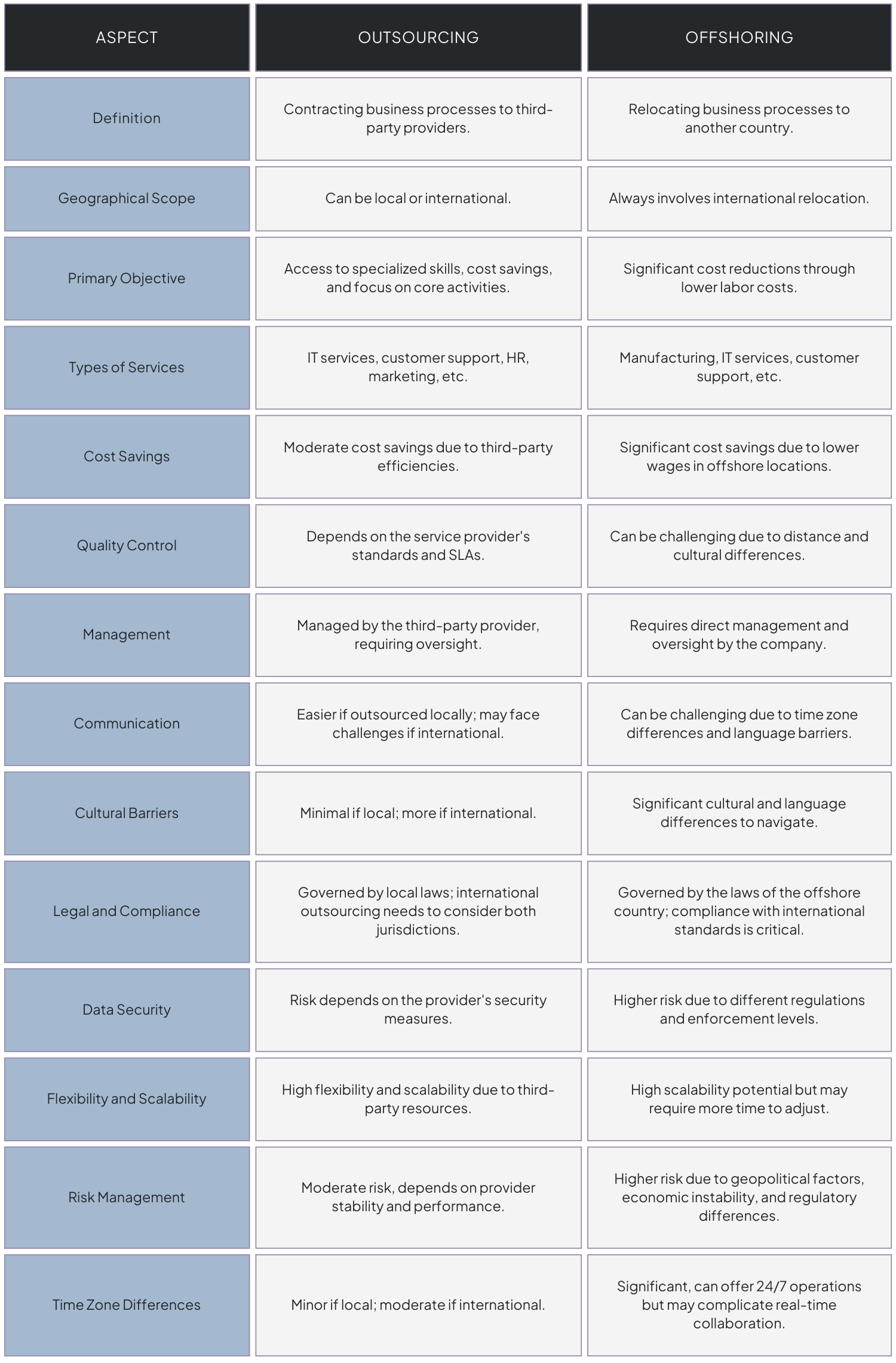
Key Differences Between Outsourcing and Offshoring
Outsourcing and offshoring are two business strategies often used to optimize operations, reduce costs, and enhance efficiency. Here’s a detailed comparison of the two in terms of various aspects:
1. Geographical Scope
Outsourcing: Involves contracting services to a third-party company, which can be located domestically or internationally. The primary focus is on leveraging specialized skills and services outside the organization.
Offshoring: Specifically involves relocating business processes or services to a different country, usually to take advantage of lower labor costs or other economic benefits. This always involves an international component.
2. Primary Objective
Outsourcing: Aims to reduce costs, improve efficiency, and focus on core business functions by leveraging external expertise and resources.
Offshoring: Primarily seeks to reduce operational costs by taking advantage of lower wages and favorable economic conditions in other countries.
3. Types of Services
Outsourcing: Can include a wide range of services such as IT support, customer service, HR functions, marketing, and more. The focus is on finding the best provider for specific services, regardless of location.
Offshoring: Commonly involves IT services, manufacturing, and back-office functions like accounting and data processing, specifically moved to countries with cost advantages.
4. Cost Savings
Outsourcing: Achieves cost savings through reduced labor costs, operational efficiencies, and avoidance of expenses related to hiring, training, and infrastructure.
Offshoring: Offers significant cost savings by moving operations to countries with lower labor costs and reduced operational expenses, sometimes at the expense of higher management and coordination costs.
In both cases, clear communication, setting expectations, and using the right tools are key to successful management.
5. Quality Control
Outsourcing: Quality depends on the service provider’s expertise and adherence to agreed-upon standards. Contracts typically include quality benchmarks and service-level agreements (SLAs).
Offshoring: Quality control can be more challenging due to distance and potential differences in standards. Strong management and clear SLAs are crucial to maintaining quality.
6. Management
Outsourcing: Managed through contracts with defined terms, performance metrics, and regular reviews. The outsourcing company handles day-to-day management of their employees.
Offshoring: Requires more hands-on management from the parent company, including overseeing operations, maintaining communication, and ensuring alignment with business objectives.
8. Cultural Barriers
Outsourcing: Cultural differences can exist but are less pronounced if the service provider is in a similar cultural context or domestic market.
Offshoring: Significant cultural differences may impact business practices, communication, and work expectations. Cultural training and sensitivity are important for smooth operations.
9. Legal and Compliance
Outsourcing: Compliance with domestic laws and regulations is typically more straightforward, though international outsourcing requires attention to different legal systems.
Offshoring: Requires navigating complex international legal and regulatory environments, including labor laws, tax regulations, and trade agreements.
10. Data Security
Outsourcing: Data security concerns depend on the provider’s policies and location. Domestic providers may offer higher confidence in data security standards.
Offshoring: Heightened data security risks due to varying international data protection laws. Ensuring compliance with data protection regulations and robust security measures is critical.
11. Flexibility and Scalability
Outsourcing: Offers high flexibility and scalability by allowing businesses to quickly adjust the level of service based on demand without long-term commitments.
Offshoring: Provides scalability, particularly in terms of labor, but may face challenges in flexibility due to logistical complexities and time required to set up offshore operations.
12. Risk Management
Outsourcing: Risks include potential loss of control over the outsourced functions, dependency on the service provider, and possible breaches of confidentiality.
Offshoring: Adds risks related to political instability, exchange rate fluctuations, and the complexity of managing international operations. Diversification and robust contingency plans are essential.
13. Timezone Differences
Outsourcing: Timezone differences can be minimal or significant depending on the provider’s location. Nearshore outsourcing minimizes timezone challenges.
Offshoring: Often involves substantial timezone differences, which can lead to coordination challenges. However, it can also provide the advantage of round-the-clock operations.
Offshoring vs. Outsourcing Table Comparison
Types of Services Commonly Offshored
Whether you’re a startup or a large enterprise, there are numerous services that can be efficiently managed by external experts or overseas teams. Let’s explore the types of services that are commonly outsourced and offshored.
1. Information Technology (IT) Services
Offshored Services:
- Application Development and Maintenance: Offshoring these tasks can significantly reduce costs while leveraging a global talent pool.
- Data Center Operations: Managing data centers in countries with lower operational costs helps in maintaining budgets without compromising on quality.
2. Customer Support
Offshored Services:
- 24/7 Customer Service: With teams in different time zones, businesses can offer round-the-clock support to customers worldwide.
- Multilingual Support: Offshoring to regions with multilingual capabilities can enhance customer satisfaction and expand market reach.
3. Human Resources (HR) Services
Offshored Services:
- Talent Acquisition: Offshoring talent acquisition tasks can help in tapping into global talent pools and reducing hiring costs.
- HR Compliance: Ensuring compliance with local labor laws through offshore teams helps in mitigating risks.

Exploring the Role of AI in Outsourcing: Is It Still Necessary?
In the age of Artificial Intelligence (AI), outsourcing is not just relevant; it’s becoming increasingly strategic. Explore how AI complements human expertise, reshaping traditional outsourcing
4. Finance and Accounting
Offshored Services:
- Financial Analysis: Offshoring financial analysis can provide detailed insights at a lower cost.
- Audit Services: Conducting audits through offshore teams can ensure thoroughness and impartiality.
5. Digital Marketing
Offshored Services:
- Pay-Per-Click (PPC) Management: Managing PPC campaigns through offshore teams can optimize advertising budgets and improve ROI.
- Graphic Design: Offshore graphic designers can create visually appealing materials at a fraction of the cost.
6. Administrative Services
Offshored Services:
- Document Management: Managing documents through offshore teams can enhance organization and reduce overhead costs.
- Transcription Services: Offshore transcription services provide accurate and timely transcriptions at lower rates.
How Can Offshoring Benefit Your Business?
In today’s fast-paced landscape, offshore outsourcing isn’t just a buzzword, it’s a proven, cost-effective way to supercharge your business operations. Whether you’re running a call center or scaling tech support, many companies are discovering that moving business operations to another country gives them access to a skilled workforce without draining resources in their home country.
But here’s where it gets real: the difference between offshoring with just anyone and offshoring with the right partner can make or break your results.
That’s where iScale Solutions comes in. With strategic offshore locations and a tailored approach, we help your company stay agile, efficient, and focused on what actually matters. So if your company might be considering the leap, let’s talk about how to do it smart.
Want to know how offshore outsourcing can work for you? Contact iScale Solutions today and make your business future-ready.


