In today’s interconnected world, businesses of all sizes are increasingly looking to expand their operations beyond domestic borders. This global expansion presents a wealth of opportunities, including access to new markets, a broader customer base, and the ability to tap into diverse talent pools.
However, with these opportunities come significant challenges, particularly when it comes to managing an international workforce. Navigating different labor laws, tax regulations, and payroll systems can be daunting and time-consuming.
To address these complexities, businesses often turn to specialized services such as wage hosting and employer of record (EOR). These solutions are designed to simplify the management of remote teams and ensure compliance with local employment laws, allowing companies to focus on their core operations.
In this article, we will explore the differences between wage hosting and EOR services, highlighting their benefits, limitations, and the scenarios in which each might be the best fit for your business needs.
What is Wage Hosting?
Wage hosting is a specialized service designed to streamline payroll management for businesses, particularly those with employees in multiple locations. At its core, wage hosting involves a third-party provider handling the complexities of payroll processing, ensuring that employees are paid accurately and on time while complying with local tax laws and regulations.
How Wage Hosting Works
When a company engages a wage hosting service, the provider takes on the responsibility of managing payroll for the company’s employees. This includes calculating wages, processing payments, and handling deductions for taxes and benefits.
The wage hosting provider acts as an intermediary between the company and its employees, ensuring that all payroll-related activities are executed smoothly and efficiently.
Key Services Provided Under Wage Hosting
- Payroll Processing: The provider calculates employee wages based on hours worked, salary agreements, and any applicable overtime. They ensure that payments are made promptly and accurately, reducing the risk of payroll errors.
- Tax Deductions: Wage hosting services manage all tax-related deductions, including federal, state, and local taxes. They ensure compliance with tax laws and handle the filing of necessary tax documents.
- Compliance: Staying compliant with local labor laws and regulations can be challenging, especially for companies operating in multiple regions. Wage hosting providers ensure that payroll practices adhere to all relevant legal requirements, minimizing the risk of penalties and fines.
- Benefits Management: Some wage hosting services also manage employee benefits, such as health insurance, retirement plans, and other perks. This includes administering contributions and ensuring compliance with benefits regulations.
- Reporting and Record-Keeping: Accurate record-keeping and regular reporting are essential for transparency and legal compliance. Wage hosting providers maintain detailed payroll records and provide regular reports to the company, aiding in financial planning and audits.
Benefits of Wage Hosting
Efficiency in Payroll Management
One of the primary benefits of wage hosting is the increased efficiency in managing payroll processes. Wage hosting providers use advanced systems and software to handle payroll tasks swiftly and accurately. This reduces the administrative burden on internal HR departments, allowing them to operate more effectively and dedicate their time to strategic initiatives.
Ensures Compliance with Local Tax Laws
Wage hosting providers are experts in local tax requirements and ensure that all payroll practices adhere to the relevant laws. This compliance minimizes the risk of legal issues, penalties, and fines, providing peace of mind to business owners.
Reduces Payroll Errors
Accuracy is crucial in payroll management, as errors can lead to employee dissatisfaction and potential legal challenges. Wage hosting providers utilize precise and reliable payroll systems, significantly reducing the likelihood of mistakes in wage calculations and deductions. This accuracy ensures that employees are paid correctly and on time, fostering a positive work environment.
Allows Businesses to Focus on Core Activities
By outsourcing payroll management to a wage hosting provider, businesses can free up valuable time and resources. This allows company leaders and HR teams to concentrate on core business activities and strategic growth initiatives rather than getting bogged down in administrative payroll tasks. With payroll efficiently managed, businesses can enhance productivity and focus on achieving their broader goals.
Limitations of Wage Hosting
While wage hosting provides numerous benefits in terms of efficiency and compliance, it also has certain limitations that businesses need to consider. Understanding these limitations can help companies determine whether wage hosting is the right solution for their specific needs.
Limited to Payroll Management
The primary focus of wage hosting is on managing payroll processes. While this includes calculating wages, processing payments, and handling tax deductions, wage hosting does not extend beyond these functions. This means that other critical aspects of employment, such as employee relations, performance management, and career development, are not covered by wage hosting services. Companies still need to manage these HR functions internally or seek additional services to handle them.
The Original Company Remains the Legal Employer
Under a wage hosting arrangement, the original company retains its status as the legal employer of the workforce. This means that the company is still responsible for adhering to local labor laws and regulations, maintaining employment contracts, and managing any legal issues that may arise. While the wage hosting provider handles payroll, the company must ensure compliance with broader employment laws and standards, which can be complex and demanding.
Does Not Cover Employee Benefits, Contracts, or HR Support
What is an Employer of Record (EOR)?
An Employer of Record (EOR) is a third-party organization that takes on the legal responsibilities of employing workers on behalf of a company. This service is particularly beneficial for businesses looking to expand into new regions or countries without establishing a legal entity there. By acting as the legal employer, the EOR allows companies to hire and manage employees in different locations while ensuring compliance with local laws and regulations.
How EOR Works
When a company partners with an EOR, the EOR becomes the official employer for the company’s international workforce. While the company retains control over day-to-day work activities and management, the EOR company handles all employment-related tasks. This includes everything from payroll and benefits administration to tax compliance and human resources management. Essentially, the EOR assumes the legal and administrative burdens of employment, enabling the company to focus on its core operations.
Key Services Provided Under EOR
- Payroll Management: The EOR processes employee payroll, ensuring accurate and timely payments. This includes calculating wages, handling deductions, and ensuring compliance with local tax laws.
- Benefits Administration: EORs manage employee benefits such as health insurance, retirement plans, and other perks. They ensure that all benefits are provided in accordance with local regulations and company policies.
- Tax Compliance: Navigating the complexities of tax regulations in different regions can be challenging. EORs ensure that all necessary tax withholdings, filings, and payments are handled correctly, reducing the risk of penalties and fines.
- HR Management: EORs provide comprehensive human resources support, including onboarding, employee relations, performance management, and terminations. They ensure that all HR processes are compliant with local labor laws and best practices.
- Employment Contracts: The EOR drafts and maintains employment contracts in accordance with local legal requirements. This includes ensuring that contracts are legally binding and protect both the employee and the employer.
- Legal Compliance: EORs stay up-to-date with local labor laws and regulations, ensuring that the company remains compliant at all times. This mitigates the risk of legal issues and ensures smooth operation in new markets.
- Work Permits and Visas: For businesses hiring international talent, EORs handle the complexities of obtaining work permits and visas, ensuring that employees can legally work in their respective countries.
Benefits of an Employer of Record (EOR)
Comprehensive Management of HR Functions
One of the most significant advantages of an EOR is the comprehensive management of HR functions. The EOR handles everything from payroll processing and benefits administration to employee onboarding and termination. This includes drafting and maintaining employment contracts, managing employee relations, and ensuring that all HR practices comply with local labor laws. By outsourcing these tasks to an EOR, businesses can reduce the administrative burden on their internal HR teams and ensure that all HR functions are managed efficiently and effectively.
Ensures Full Legal Compliance
An EOR stays up-to-date with all relevant laws and ensures that the company remains fully compliant at all times. This includes handling tax withholdings, filings, and payments, as well as managing work permits and visas for international employees. By ensuring full legal compliance, an EOR mitigates the risk of legal issues, penalties, and fines, providing peace of mind to business owners.
Facilitates Quick Market Entry
Mitigates Risks Associated with Non-Compliance
Non-compliance with local labor laws can result in significant risks, including legal disputes, financial penalties, and reputational damage. An EOR mitigates these risks by ensuring that all employment practices are compliant with local laws and regulations. This includes managing employee benefits, handling tax obligations, and maintaining accurate and up-to-date employment records. By outsourcing compliance to an EOR, businesses can avoid the pitfalls of non-compliance and focus on their strategic objectives.
Are you ready to simplify your payroll and compliance processes?
Limitations of an Employer of Record (EOR)
Reduced Control Over Employment Practices
Potentially Higher Costs
Dependence on a Third Party for Significant Business Operations
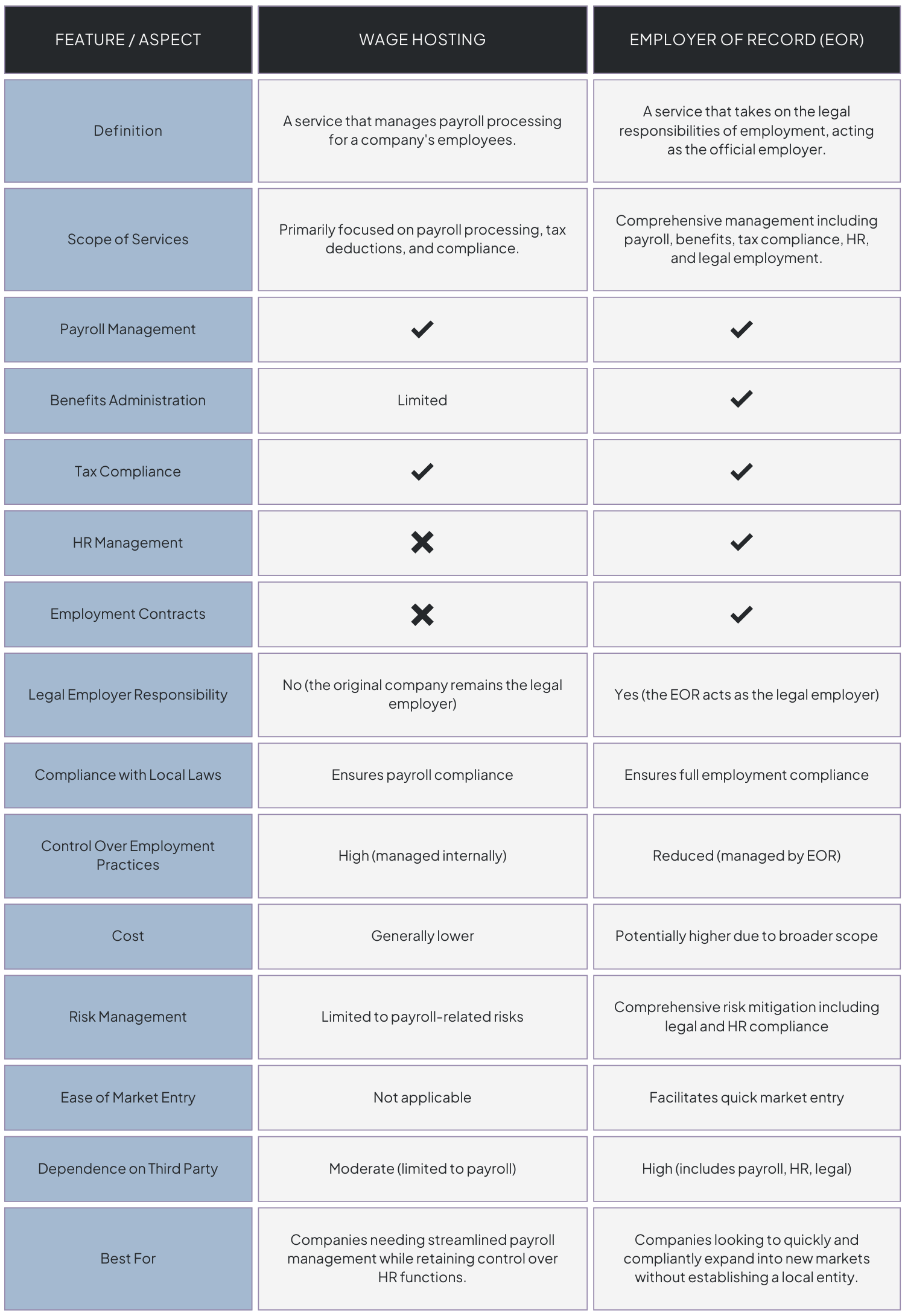
Wage Hosting vs. Employer of Record
To help your understand the key differences between wage hosting and Employer of Record (EOR) services, here’s a table that highlights the main features, benefits, and limitations of each service, enabling companies to make an informed decision based on their specific needs and goals.
Which Service is Right for Your Business?
Choosing between wage hosting and Employer of Record (EOR) services depends on your company’s specific needs, goals, and operational context. Here are some situations to help determine which service might be more suitable for your business.
When Wage Hosting is More Suitable
- Domestic Expansion: If your business is expanding within your home country and you only need assistance with payroll processing and compliance, wage hosting is an efficient solution. It allows you to handle other HR functions internally while ensuring accurate and compliant payroll management.
- Established Local Presence: Companies that already have a legal entity and a well-established HR infrastructure in a particular country might only need help with payroll complexities. Wage hosting can streamline payroll processes without interfering with existing HR practices.
- Maintaining HR Control: If retaining control over employment practices, employee relations, and company culture is crucial, wage hosting is preferable. It allows you to manage most HR functions in-house while outsourcing payroll tasks to experts.
- Cost-Sensitive Operations: Businesses with tight budgets that need to optimize operational costs may find wage hosting more cost-effective than EOR. Since wage hosting focuses on payroll, it typically involves lower fees compared to the comprehensive services of an EOR.
When an EOR is More Beneficial
- Global Expansion: If your business is looking to expand internationally without establishing a legal entity in each new country, an EOR is the best solution. It allows you to quickly and compliantly hire employees in new markets, facilitating rapid market entry and growth.
- Comprehensive HR Management: For companies that need extensive HR support, including benefits administration, employment contracts, and compliance with local labor laws, an EOR provides a complete package. This is especially beneficial for businesses lacking internal HR expertise in foreign markets.
- Risk Mitigation: Companies operating in highly regulated industries or regions with complex labor laws can benefit from the risk mitigation provided by an EOR. The EOR ensures full compliance with local laws, reducing the risk of legal issues and penalties.
- Resource Constraints: If your company has limited internal resources to manage HR functions and compliance in new markets, an EOR offers a turnkey solution. By outsourcing these responsibilities, you can focus on strategic objectives without being bogged down by administrative tasks.
Making the Right Choice
To determine the best service for your business, consider the following factors:
- Business Goals: Identify whether your primary goal is to expand quickly into new markets, streamline payroll processes, or maintain control over HR functions.
- Operational Scope: Assess whether you need a comprehensive HR management solution or if your needs are limited to payroll processing and compliance.
- Budget: Evaluate your budget constraints and determine if the cost of an EOR aligns with the benefits it provides compared to wage hosting.
- Internal Resources: Consider the availability and capability of your internal HR team to manage employment-related tasks, especially in foreign markets.
- Compliance Needs: Determine the complexity of local labor laws in the regions where you operate and your ability to manage compliance internally.
Conclusion
Wage hosting and Employer of Record (EOR) services both offer solutions for managing a global workforce. Wage hosting focuses on payroll, making it ideal for companies wanting control over HR functions. EOR provides comprehensive services, including payroll, benefits, HR management, and legal compliance, perfect for businesses expanding internationally without a legal entity.
Choosing the right service is crucial. Wage hosting suits those needing efficient payroll services, while EOR is best for comprehensive management across multiple countries. Assess your business needs, budget, and goals to ensure effective workforce management.
For tailored solutions, consider partnering with iScale Solutions. Contact us today to learn more.

